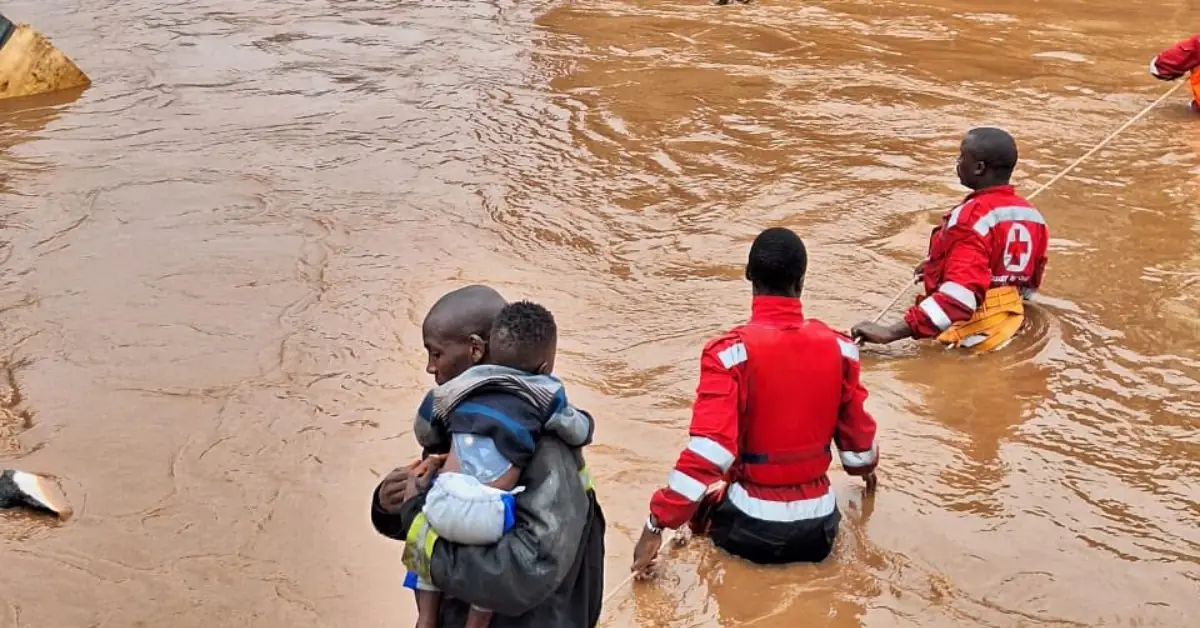
Kenya nairobi flooding – Nairobi’s Flooding Crisis: Causes, Consequences, and Mitigation. Nairobi, the bustling capital of Kenya, has been grappling with the devastating effects of flooding for decades. The city’s infrastructure, environmental degradation, and socioeconomic challenges have all contributed to this ongoing crisis, leading to widespread damage, displacement, and loss of life.
This article delves into the complexities of Nairobi’s flooding crisis, exploring the root causes, far-reaching consequences, and innovative strategies being employed to mitigate its impact. By understanding the challenges and potential solutions, we can work towards a more resilient and flood-proof Nairobi.
Nairobi’s Infrastructure and Flooding
Nairobi’s infrastructure, including drainage systems and urban planning, plays a crucial role in flooding. Poor drainage, inadequate waste management, and unplanned development contribute to the city’s vulnerability to flooding.
Drainage Systems and Flooding
Nairobi’s drainage systems are often overwhelmed during heavy rainfall, leading to flooding. The city’s aging infrastructure and lack of regular maintenance exacerbate the problem. Additionally, poor waste management practices, such as littering and illegal dumping, block drains and worsen flooding.
Urban Planning and Development, Kenya nairobi flooding
Unplanned urban development, including the construction of buildings and roads in flood-prone areas, further contributes to flooding. The lack of green spaces and permeable surfaces reduces water absorption and increases runoff, exacerbating flooding.
Causes of Flooding in Nairobi: Kenya Nairobi Flooding
Heavy Rainfall
Nairobi experiences heavy rainfall during the rainy seasons, which can lead to flooding. The city’s location in a valley surrounded by hills makes it prone to flash floods and waterlogging.
Poor Drainage
As discussed earlier, Nairobi’s drainage systems are inadequate and poorly maintained, contributing to flooding. Blockages, aging infrastructure, and lack of capacity lead to water accumulation and flooding.
Inadequate Waste Management
Poor waste management practices, including littering, illegal dumping, and inadequate waste collection, block drains and waterways, exacerbating flooding. Solid waste can clog drainage systems, preventing water from flowing freely.
Climate Change and Deforestation
Climate change is leading to more frequent and intense rainfall events, increasing the risk of flooding. Deforestation in the surrounding areas reduces water absorption and increases runoff, contributing to flooding downstream.
Socioeconomic Factors
Informal settlements and poverty also play a role in flooding. Informal settlements are often located in flood-prone areas, and residents lack access to adequate housing and infrastructure, making them more vulnerable to flooding.
Consequences of Flooding in Nairobi
Immediate Consequences
- Property damage: Flooding can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
- Displacement: Flooding can force people to evacuate their homes and seek shelter elsewhere.
- Health hazards: Standing water can breed mosquitoes and other disease-carrying insects, posing health risks to communities.
Long-Term Consequences
- Economic losses: Flooding can disrupt businesses, damage infrastructure, and affect livelihoods, leading to economic losses.
- Social and psychological impacts: Flooding can cause stress, anxiety, and trauma, affecting the well-being of communities.
- Environmental degradation: Flooding can pollute water sources, damage ecosystems, and displace wildlife.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Mitigation Strategies
- Flood warning systems: Implementing early warning systems to alert communities to impending floods.
- Drainage improvements: Upgrading and expanding drainage systems to increase water flow and reduce flooding.
- Green infrastructure: Creating green spaces, such as parks and rain gardens, to absorb rainwater and reduce runoff.
Adaptation Strategies
- Water-sensitive urban design: Designing cities with permeable surfaces and rainwater harvesting systems to manage stormwater.
- Relocation and resettlement: Moving communities from flood-prone areas to safer locations.
- Community-based initiatives: Engaging local communities in flood preparedness and response efforts.
Role of Stakeholders in Flood Management

Key Stakeholders
- Government agencies: Responsible for developing and implementing flood management policies and regulations.
- NGOs: Provide support to communities affected by flooding and advocate for flood prevention measures.
- Community organizations: Mobilize communities and engage in flood preparedness and response efforts.
Collaboration and Coordination
Effective flood management requires collaboration and coordination among stakeholders. This includes sharing information, resources, and expertise to improve flood preparedness and response.
Best Practices and Lessons Learned
Best Practices from Other Cities
- Singapore: Implemented a comprehensive flood management system, including a network of canals and reservoirs.
- London: Built a massive underground tunnel system to divert excess stormwater.
- Rotterdam: Raised buildings and infrastructure to adapt to rising sea levels and flooding.
Lessons Learned from Nairobi
- The importance of early warning systems and community preparedness.
- The need for sustainable urban planning and development to reduce flooding risks.
- The role of community-based initiatives in mitigating and responding to flooding.
Ultimate Conclusion
Nairobi’s flooding crisis is a multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach. By addressing the underlying causes, investing in resilient infrastructure, and empowering communities, we can build a more sustainable and flood-resilient Nairobi for future generations.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the primary causes of flooding in Nairobi?
Nairobi’s flooding is primarily caused by a combination of factors, including heavy rainfall, poor drainage systems, inadequate waste management, deforestation, and urbanization.
What are the consequences of flooding in Nairobi?
Flooding in Nairobi has severe consequences, including damage to property and infrastructure, displacement of residents, disruption of livelihoods, and increased health risks.
What are some mitigation strategies being implemented in Nairobi to reduce flooding?
Nairobi has implemented various mitigation strategies, such as improving drainage systems, constructing flood control structures, and implementing early warning systems.